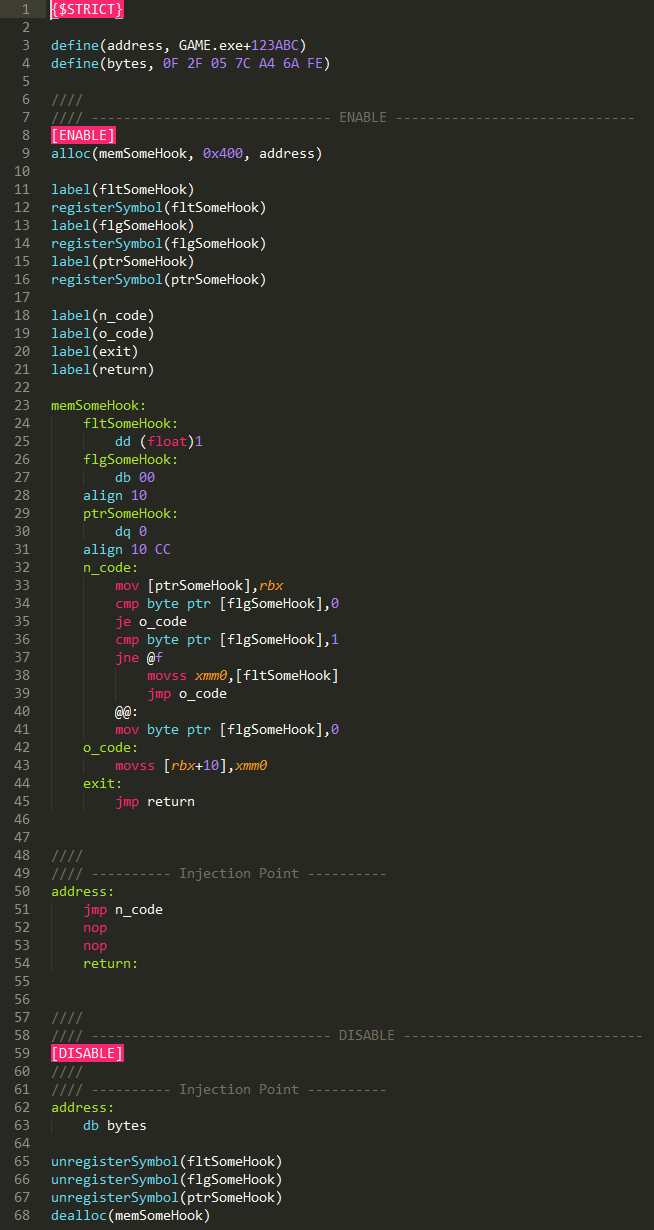
Auto Assembler - Example 2
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Let's look at that the following example.
- Note: All numbers in the Auto Assembler are read as hexadecimal format by default, use # or (int) for decimal format (base 10).
- Note: Values written in a 0x* notation are in hexadecimal format.
Main section[edit]
- 1. {$STRICT}
- When {$STRICT} is present in your script, Cheat Engine will not assume that an undefined symbol is a label, and will give you an error instead.
- Note that this is optional.
- 3. define(address, GAME.exe+123ABC)
- This line defines or sets "address" to "GAME.exe+123ABC",
- i.e.: any where in this script we place "address" Cheat Engine will replace it with "GAME.exe+123ABC".
- 4. define(bytes, 0F 2F 05 7C A4 6A FE)
- This line defines or sets "bytes" to "0F 2F 05 7C A4 6A FE",
- i.e.: any where in this script we place "bytes" Cheat Engine will replace it with "0F 2F 05 7C A4 6A FE".
Enable section[edit]
- 8. [ENABLE]
- This line just denotes the start of the enable section.
- Note: Cheat Engine table scripts require an enable and disable section.
- 9. alloc(memSomeHook, 0x400, address)
- This line allocates 0x400 bytes using the symbol "memSomeHook", near the address of address (which is "GAME.exe+123ABC").
- 11. label(fltSomeHook)
- This creates a label using the symbol "fltSomeHook".
- 12. registerSymbol(fltSomeHook)
- This registers the symbol "fltSomeHook" with the user symbol list.
- A registered symbol can be used in the disable section and else where on the table.
- 13. label(flgSomeHook)
- This creates a label using the symbol "flgSomeHook".
- 14. registerSymbol(flgSomeHook)
- This registers the symbol "flgSomeHook" with the user symbol list.
- 15. label(ptrSomeHook)
- This creates a label using the symbol "ptrSomeHook".
- 16. registerSymbol(ptrSomeHook)
- This registers the symbol "ptrSomeHook" with the user symbol list.
- 18. label(n_code)
- This creates a label using the symbol "n_code".
- 19. label(o_code)
- This creates a label using the symbol "o_code".
- 20. label(exit)
- This creates a label using the symbol "exit".
- 21. label(return)
- This creates a label using the symbol "return".
- 23. memSomeHook∶
- This places the symbol, here it denotes to start assembling at the address of memSomeHook.
- 24. fltSomeHook∶
- This places the symbol, here it denotes the placement of fltSomeHook.
- 25. dd (float)1
- This sets the size of the "fltSomeHook" as a data double word (4 bytes), with a float value of 1.
- 26. flgSomeHook∶
- This places the symbol, here it denotes the placement of flgSomeHook.
- 27. db 00
- This sets the size of the "flgSomeHook" as a data byte, with a value of 0.
- 28. align 10
- This will align what comes after this line, it aligns at an address ending with 0x10, with the default padding byte of 0x0.
- 29. ptrSomeHook∶
- This places the symbol, here it denotes the placement of ptrSomeHook.
- 30. dq 0
- This sets the size of the "ptrSomeHook" as a data quadword (8 bytes), with a value of 0x0.
- Note: ptrSomeHook will be used as a base address and in 64 bit mode 8 bytes is needed, but in 32 bit mode only 4 bytes is needed.
- 31. align 10 CC
- This will align what comes after this line, it aligns at an address ending with 0x10, with a padding byte of 0xCC.
- 32. n_code∶
- This places the symbol, here it denotes the placement of n_code, this will be the start of the new code.
- 33. mov [ptrSomeHook],rbx
- This will move the value of RBX into the value at the address (denoted by the [ and ]) of ptrSomeHook.
- 34. cmp byte ptr [flgSomeHook],0
- This compares a byte pointer value at the address of flgSomeHook to 0x0 (as an immediate).
- 35. je o_code
- This will jump, if equal to the label o_code; i.e.: if the last compare equated to being equal.
- 36. cmp byte ptr [flgSomeHook],1
- This compares a byte pointer value at the address of flgSomeHook to 0x1.
- 37. jne @f
- This will jump, if not equal forward to the next label (denoted by the "@f", as "@b" would be for a label back); i.e.: if the last compare equated to being not equal.
- 38. movss xmm0,[fltSomeHook]
- This will move a Scalar Single-Precision Floating-Point of the value at the address of fltSomeHook into XMM0.
- 39. jmp o_code
- This will jump to the label o_code.
- 40. @@∶
- This denotes a generic label, it can't be used by name is only useful with "@f" and "@b".
- 41. mov byte ptr [flgSomeHook],0
- This will move a byte value of 0x0 into the value at the address of flgSomeHook.
- 42. o_code∶
- This places the symbol, here it denotes the placement of o_code, this will be the start of the original code.
- 43. movss [rbx+10],xmm0
- This will move a Scalar Single-Precision Floating-Point of XMM0 into the value at the address of RBX plus 0x10.
- 44. exit∶
- This places the symbol, here it denotes the placement of exit, this will be the start of the exit code, note that the exit label is not used so it could be removed with the label declaration.
- 45. jmp return
- This will jump to the label return.
- 50. address∶
- This places the symbol, here it denotes to start assembling at the address of address (which is "GAME.exe+123ABC").
- 51. jmp n_code
- This will jump to the label n_code. This is the injection hook, as it hooks the code to do some thing else.
- Note that, in 64 bit mode, here is where the use of AllocateNearThisAddress with alloc helps to insure a 5 byte jump.
- 52. nop
- This is a NOP (no operation), here it is used a padding as the original instruction was more then 5 bytes
- 54. return∶
- This places the symbol, here it denotes the placement of return, this will be the return point.
Disable section[edit]
- 59. [DISABLE]
- This line just denotes the start of the disable section.
- 62. address∶
- This places the symbol, here it denotes to start assembling at the address of address (which is "GAME.exe+123ABC").
- 63. db bytes
- This denotes to start assembling data bytes using the symbol bytes (which is "0F 2F 05 7C A4 6A FE").
- 65. unregisterSymbol(fltSomeHook)
- This unregisters the symbol "fltSomeHook" with the user symbol list.
- 66. unregisterSymbol(flgSomeHook)
- This unregisters the symbol "flgSomeHook" with the user symbol list.
- 67. unregisterSymbol(ptrSomeHook)
- This unregisters the symbol "ptrSomeHook" with the user symbol list.
- 68. dealloc(memSomeHook)
- This deallocates the memory at "memSomeHook".