Difference between revisions of "Assembler:Commands:CALL"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''command''' call '' | + | [[Category:Assembler]] |
| + | '''command''' call ''size'' ''operand'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Calls the given operand (address or function), jumps to the given operand then returns. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: A RET must be hit for a CALL to work properly, best to use JMPs if unsure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="padding:2px;border:1px dashed #2f6fab;background-color:#f4f4f4;"> | ||
| + | Saves procedure linking information on the stack and branches to the procedure (called procedure) | ||
| + | specified with the destination (target) operand. | ||
| + | The target operand specifies the address of the first instruction in the called procedure. | ||
| + | This operand can be an immediate value, a general purpose register, or a memory location. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This instruction can be used to execute four different types of calls: | ||
| + | ; Near call | ||
| + | : A call to a procedure within the current code segment (the segment currently pointed to by the CS register), sometimes referred to as an intrasegment call. | ||
| + | ; Far call | ||
| + | : A call to a procedure located in a different segment than the current code segment, sometimes referred to as an intersegment call. | ||
| + | ; Inter-privilege-level far call | ||
| + | : A far call to a procedure in a segment at a different privilege level than that of the currently executing program or procedure. | ||
| + | ; Task switch | ||
| + | : A call to a procedure located in a different task. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://c9x.me/x86/html/file_module_x86_id_26.html c9x.me/x86/html/file_module_x86_id_26.html] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Command Parameters === | === Command Parameters === | ||
| Line 10: | Line 32: | ||
!style="width: 80%;background-color:white;" align="left"|Description | !style="width: 80%;background-color:white;" align="left"|Description | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |size '''OPTIONAL''' |
|The preferred size of the assembled address | |The preferred size of the assembled address | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 37: | Line 59: | ||
call long someLabel // Call the label with full address. | call long someLabel // Call the label with full address. | ||
| − | call @b // Call back the closest | + | call @b // Call back the closest label |
| + | |||
| + | call @f // Call forward the closest label | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Running this script in 32 bit mode: | ||
| + | globalAlloc(memTest, 0x200) | ||
| + | label(testLbl) | ||
| + | memTest: | ||
| + | add [eax],al // db 00 00 | ||
| + | @@: | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | ret | ||
| + | call short @b | ||
| + | call short @f | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | @@: | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | ret | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | call short -8 | ||
| + | call short +2 | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | testLbl: | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | ret | ||
| + | call 02EA0002 | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | call eax | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | call memTest | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | call testLbl | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | call short testLbl | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | call long testLbl | ||
| + | add [eax],al | ||
| + | db 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 | ||
| − | + | [[File:Assembler.CALL.02.png]] | |
| Line 76: | Line 136: | ||
add [rax],al | add [rax],al | ||
db 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 | db 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 | ||
| − | |||
[[File:Assembler.CALL.01.png]] | [[File:Assembler.CALL.01.png]] | ||
| − | + | {{AssemblerCommandSeeAlso}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{Template:AssemblerCommandExternalLinks}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 15:40, 3 January 2018
command call size operand
Calls the given operand (address or function), jumps to the given operand then returns.
Note: A RET must be hit for a CALL to work properly, best to use JMPs if unsure.
Saves procedure linking information on the stack and branches to the procedure (called procedure) specified with the destination (target) operand. The target operand specifies the address of the first instruction in the called procedure. This operand can be an immediate value, a general purpose register, or a memory location.
This instruction can be used to execute four different types of calls:
- Near call
- A call to a procedure within the current code segment (the segment currently pointed to by the CS register), sometimes referred to as an intrasegment call.
- Far call
- A call to a procedure located in a different segment than the current code segment, sometimes referred to as an intersegment call.
- Inter-privilege-level far call
- A far call to a procedure in a segment at a different privilege level than that of the currently executing program or procedure.
- Task switch
- A call to a procedure located in a different task.
Command Parameters[edit]
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| size OPTIONAL | The preferred size of the assembled address |
| operand | The address or symbol to call |
Examples[edit]
call +1A // Call from end of command to +1A (hex).
call 00123ABC // Call the address.
call 0000123456ABCDEF // Call the address.
call eax // Call the value of eax.
call rax // Call the value of rax.
call someSymbol // Call the user defined symbol.
call someLabel // Call the label.
call short someLabel // Call the label with short byte code.
call long someLabel // Call the label with full address.
call @b // Call back the closest label
call @f // Call forward the closest label
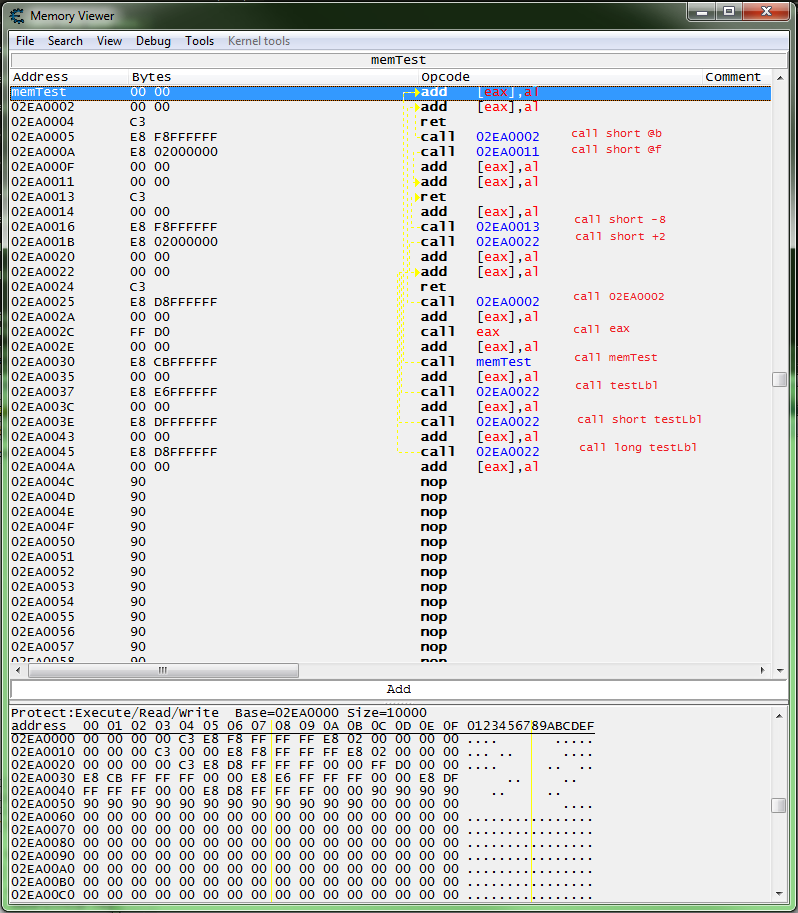
Running this script in 32 bit mode:
globalAlloc(memTest, 0x200)
label(testLbl)
memTest:
add [eax],al // db 00 00
@@:
add [eax],al
ret
call short @b
call short @f
add [eax],al
@@:
add [eax],al
ret
add [eax],al
call short -8
call short +2
add [eax],al
testLbl:
add [eax],al
ret
call 02EA0002
add [eax],al
call eax
add [eax],al
call memTest
add [eax],al
call testLbl
add [eax],al
call short testLbl
add [eax],al
call long testLbl
add [eax],al
db 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90
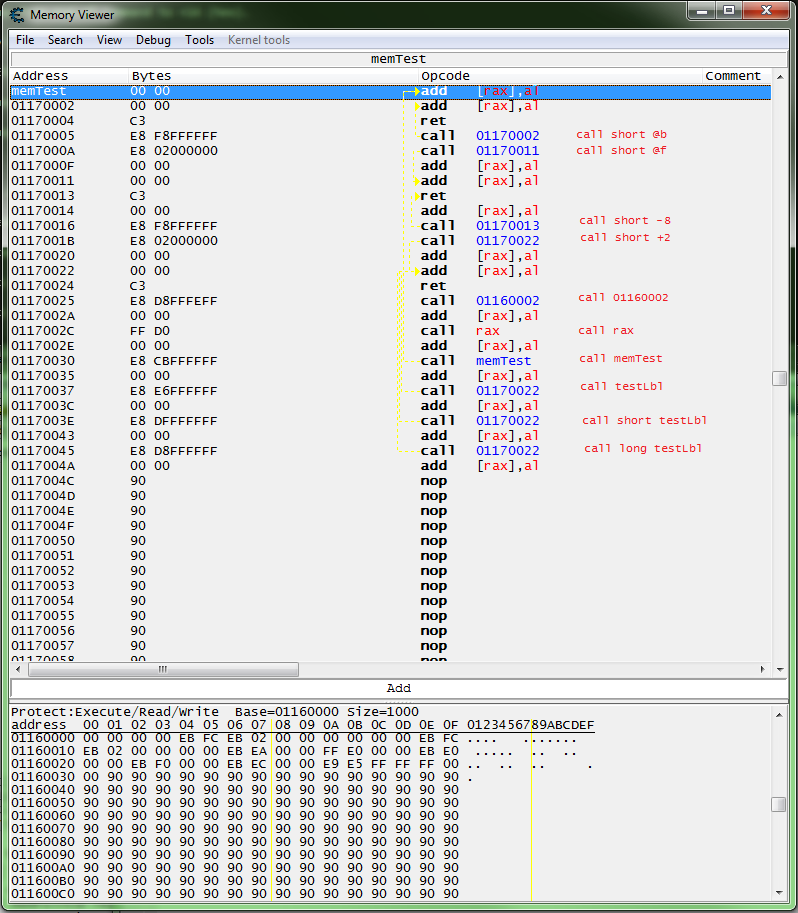
Running this script in 64 bit mode:
globalAlloc(memTest, 0x200)
label(testLbl)
memTest:
add [rax],al // db 00 00
@@:
add [rax],al
ret
call short @b
call short @f
add [rax],al
@@:
add [rax],al
ret
add [rax],al
call short -8
call short +2
add [rax],al
testLbl:
add [rax],al
ret
call 01160002
add [rax],al
call rax
add [rax],al
call memTest
add [rax],al
call testLbl
add [rax],al
call short testLbl
add [rax],al
call long testLbl
add [rax],al
db 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90 90